OUTPATIENT SERVICES
Detailed history and clinical examination helps in reaching the right diagnosis and formulating right treatment.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that checks for problems with the electrical activity of your heart. It is a simple test that can be a part of your routine health check or advised for specific cardiac complaints such as chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting or palpitations. It is best interpreted by a cardiologist along with your symptoms, clinical examination and other tests if indicated.
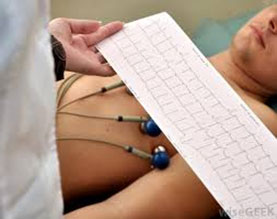 An ECG will help to
An ECG will help to
- Diagnose rhythm abnormalities with slow or fast heart rates
- Tell if you are having a heart attack or had one previously
- Find out if the heart muscles are thick (hypertrophied) especially if you have long standing high blood pressure
- Check how well heart medications are working or have side effects
- Check whether your pacemaker is functioning well
An echocardiogram, commonly called 'echo', shows the graphic detail of the heart's movement. During this test, high-frequency sound waves called ultrasound provide pictures of the heart's valves and chambers. This allows your cardiologist to evaluate the pumping action of the heart. Echo is often combined with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler test to evaluate blood flow across the heart's valves.
An echocardiogram will help to
- Assess the overall function of your heart
- Tell whether you have had a heart attack previously and the extent of damage to the heart muscle
- To assess the thickness and stiffness of heart muscles in hypertensives
- Diagnose and follow the progress of heart valve disease over time
- Evaluate the effectiveness of medical or surgical treatments
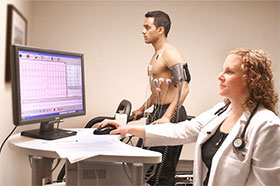 A stress test, sometimes called a treadmill test (TMT) or exercise test, helps your doctor find out how well your heart handles its workload during physical exercise. As your body works harder during the test, it requires more fuel and your heart has to pump more blood. The test can show if there's a lack of blood supply through the arteries that go to the heart.Taking a stress test also helps your doctor know the kind and level of physical activity that's right for you.
A stress test, sometimes called a treadmill test (TMT) or exercise test, helps your doctor find out how well your heart handles its workload during physical exercise. As your body works harder during the test, it requires more fuel and your heart has to pump more blood. The test can show if there's a lack of blood supply through the arteries that go to the heart.Taking a stress test also helps your doctor know the kind and level of physical activity that's right for you.
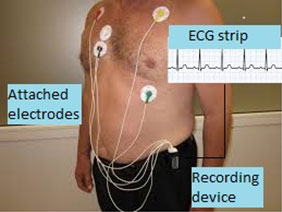 Holter Monitor involves continuous digital recording of ECG for 24 hours. The monitor can be worn during your regular daily activities. Thus it helps the physician to correlate symptoms of dizziness, palpitations or blackouts with ECG changes. It is much more likely to detect an abnormal heart rhythm as compared to the ECG alone. It can also help evaluate your ECG during episodes of chest pain, during which time there may be telltale changes to suggest reduced blood supply to the muscle of the left ventricle.
Holter Monitor involves continuous digital recording of ECG for 24 hours. The monitor can be worn during your regular daily activities. Thus it helps the physician to correlate symptoms of dizziness, palpitations or blackouts with ECG changes. It is much more likely to detect an abnormal heart rhythm as compared to the ECG alone. It can also help evaluate your ECG during episodes of chest pain, during which time there may be telltale changes to suggest reduced blood supply to the muscle of the left ventricle.
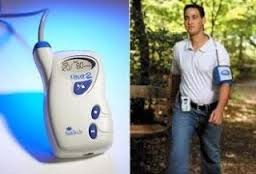 The test allows continuous monitoring of blood pressure throughout the day and is useful to determine whether you are a dipper or a non-dipper, that is to say whether or not your blood pressure falls at night as compared to daytime values. Absence of a night time dip is associated with poorer health outcomes. Also, high blood pressure in the night is associated with end organ damage
The test allows continuous monitoring of blood pressure throughout the day and is useful to determine whether you are a dipper or a non-dipper, that is to say whether or not your blood pressure falls at night as compared to daytime values. Absence of a night time dip is associated with poorer health outcomes. Also, high blood pressure in the night is associated with end organ damage
INPATIENT SERVICES
The ICCU is well equipped to treat patients with critical cardiac ailments like a heart attack, heart failure, etc
Patients symptomatic with lower heart rates need temporary pacing and can be life saving. This facility is available at the Centre
AIntraaortic balloon pump (IABP) is available for use in the ICCU and can be used in patients with cardiogenic shock
CATH LAB SERVICES
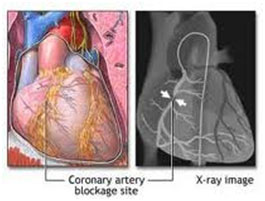 Angiography is an X-ray examination of the coronary arteries to see if they have become narrowed by fatty deposits called plaque. Plaque can decrease blood flow through a coronary artery, causing recurrent chest pain known as angina. An angiogram can also show how well the heart is functioning as a pump. Your cardiologist uses this information to plan treatment to relieve your symptoms. Treatment can include balloon angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Angiography is an X-ray examination of the coronary arteries to see if they have become narrowed by fatty deposits called plaque. Plaque can decrease blood flow through a coronary artery, causing recurrent chest pain known as angina. An angiogram can also show how well the heart is functioning as a pump. Your cardiologist uses this information to plan treatment to relieve your symptoms. Treatment can include balloon angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
 Blood flow through a coronary artery can be improved by a procedure called balloon angioplasty, which reshapes the artery's inside wall. After balloon angioplasty, your cardiologist may also insert a "stent" at the point of blockage to improve the diameter and strength of the artery. A stent is a metal scaffold and helps to increase blood flow and reduces the risk of a recurring blockage. Stent placement also decreases the need for urgent coronary artery bypass graft surgery in case a major blockage has not responded to balloon angioplasty.
Blood flow through a coronary artery can be improved by a procedure called balloon angioplasty, which reshapes the artery's inside wall. After balloon angioplasty, your cardiologist may also insert a "stent" at the point of blockage to improve the diameter and strength of the artery. A stent is a metal scaffold and helps to increase blood flow and reduces the risk of a recurring blockage. Stent placement also decreases the need for urgent coronary artery bypass graft surgery in case a major blockage has not responded to balloon angioplasty.
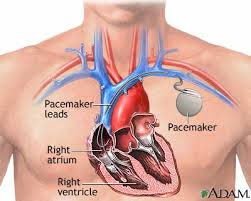 It is the implantation of a metal device underneath the skin below the collarbone using a local anaesthetic. A wire (lead) attached to the device is guided into the heart through a shoulder vein. The pacemaker provides a regular and coordinated heart rhythm in patients in whom the electrical signals in the heart have been interrupted or disorganised from disease. These patients have had dizziness, fainting episodes, blackouts or tiredness. Modern pacemakers are reliable, small and long lasting.
It is the implantation of a metal device underneath the skin below the collarbone using a local anaesthetic. A wire (lead) attached to the device is guided into the heart through a shoulder vein. The pacemaker provides a regular and coordinated heart rhythm in patients in whom the electrical signals in the heart have been interrupted or disorganised from disease. These patients have had dizziness, fainting episodes, blackouts or tiredness. Modern pacemakers are reliable, small and long lasting.
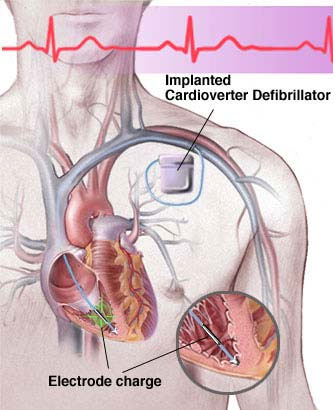 The AICD (Automated Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) is a battery operated device that is implanted beneath the skin like a pacemaker. The device continuously monitors the heart rate and rhythm. The device can recognize an abnormal heart rhythm and delivers shocks to interrupt it. Some abnormal fast heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can be life-threatening or can prevent the heart from working as an efficient pump. ICDS have saved hundreds of thousands of lives.
The AICD (Automated Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator) is a battery operated device that is implanted beneath the skin like a pacemaker. The device continuously monitors the heart rate and rhythm. The device can recognize an abnormal heart rhythm and delivers shocks to interrupt it. Some abnormal fast heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can be life-threatening or can prevent the heart from working as an efficient pump. ICDS have saved hundreds of thousands of lives.
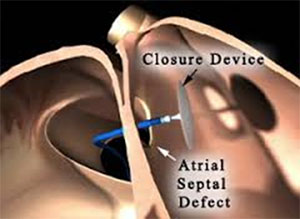 Different types of closure devices are used to close a hole or an opening between the right and left sides of the heart. Some of the common birth defects are located in the wall (septum) between the upper chambers (atria) of the heart and called atrial septal defects. The percutaneous closure of PFO and ASD is performed using a special closure device. The device is folded or attached on to a special catheter which is inserted into a vein in the leg and advanced into the heart and through the hole. The device is slowly pushed out of the special catheter allowing each side of the device to open up and cover each side of the hole (like a sandwich), closing the hole or defect. When the device is in proper position, it is released from the special catheter. Over time, heart tissue grows over the implant, becoming part of the heart. Device closures are a successful alternative to open heart surgery for such defects.
Different types of closure devices are used to close a hole or an opening between the right and left sides of the heart. Some of the common birth defects are located in the wall (septum) between the upper chambers (atria) of the heart and called atrial septal defects. The percutaneous closure of PFO and ASD is performed using a special closure device. The device is folded or attached on to a special catheter which is inserted into a vein in the leg and advanced into the heart and through the hole. The device is slowly pushed out of the special catheter allowing each side of the device to open up and cover each side of the hole (like a sandwich), closing the hole or defect. When the device is in proper position, it is released from the special catheter. Over time, heart tissue grows over the implant, becoming part of the heart. Device closures are a successful alternative to open heart surgery for such defects.
coming soon
coming soon
coming soon
coming soon


